Unlocking Seamless Token Transfers. Exploring Permit Anywhere, Permit2, and ERC2612

Preamble: The Need for Seamless and Gasless Token Approvals in DeFi
As the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem continues to grow and evolve, the demand for efficient and user-friendly token transfer mechanisms becomes increasingly critical. Traditional methods of token approvals in Ethereum-based DeFi platforms often involve multiple on-chain transactions, each incurring gas fees and adding friction to the user experience. This not only increases the cost for users but also complicates the process, making it less accessible, especially for newcomers.
Multiple protocols, boring approvals, high fees
In the fast-paced world of DeFi, where users frequently interact with multiple protocols, the inefficiency of having to manually approve each transaction can be a significant barrier. High gas fees during network congestion further exacerbate this issue, deterring users from participating in DeFi activities.
Clever ideas to onboard users in web3
To address these challenges, innovative solutions like Permit Anywhere, Permit2, and ERC2612 have been developed. These protocols introduce the concept of permit-based approvals, allowing users to authorize token transfers via off-chain signatures. This approach not only eliminates the need for multiple on-chain approval transactions but also significantly reduces gas costs, thereby enhancing the overall user experience and promoting wider adoption of DeFi services.
By enabling seamless and gasless token approvals, these protocols are paving the way for a more efficient and user-friendly DeFi ecosystem, where users can interact with various protocols effortlessly and cost-effectively.
What’s wrong with the classical approve in ERC20
As mentioned earlier the user is required first to approve its tokens to the protocol (transaction 1) and then to interact with the protocol with another transaction.
The diagram provided depicts a sequence of interactions in the context of ERC20 token transfers using a protocol contract. Here’s a detailed explanation of each step:
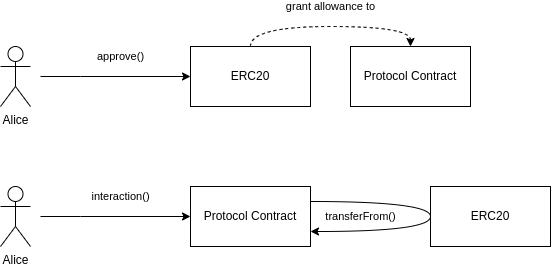
Upper Section: Granting Allowance
- Alice Approves Allowance:
- Alice (represented by the user icon on the left) initiates the process by calling the
approve()function on theERC20token contract. - This function call grants an allowance to a
Protocol Contract(indicated by the dotted line with “grant allowance to”), allowing the protocol contract to spend a certain amount of Alice’s tokens.
- Alice (represented by the user icon on the left) initiates the process by calling the
- ERC20 Contract Updates Allowance:
- The
ERC20contract updates its records to reflect that theProtocol Contractis permitted to spend a specified amount of Alice’s tokens.
- The
Lower Section: Using the Allowance
- Alice Interacts with Protocol:
- Alice initiates another interaction by calling the
interaction()function on theProtocol Contract. - This could represent any action within the protocol that requires the use of Alice’s ERC20 tokens.
- Alice initiates another interaction by calling the
- Protocol Contract Transfers Tokens:
- The
Protocol Contractthen calls thetransferFrom()function on theERC20contract. - This function transfers the tokens from Alice’s account to another account (typically the protocol’s account or another user’s account), within the limits of the previously approved allowance.
- The flow from the
Protocol Contractto theERC20contract and back indicates the successful execution of the transfer.
- The
The evolution of token permissions with ERC2612: from approve() to permit()
We have introduced this protocol in a previous post.
The diagram illustrates the workflow involving an ERC2612 token and how a permit mechanism is used to facilitate token transfer without needing an explicit on-chain approval transaction. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of the process depicted:
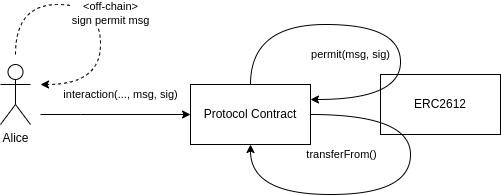
Signing the Permit
- Alice Signs Permit Message (Off-Chain):
- Alice (represented by the user icon on the left) generates a permit message off-chain. This message includes details such as the amount of tokens to be transferred and the recipient’s address.
- Alice signs this permit message using her private key. The signature (sig) authenticates her consent for the specified transaction.
Interaction with Protocol Contract
- Alice Initiates Interaction with Protocol:
- Alice sends an interaction request to the
Protocol Contract. This request includes the signed permit message (msg, sig) and any other necessary parameters. - This step effectively submits her intent to authorize the protocol to use her tokens as per the signed permit.
- Alice sends an interaction request to the
Protocol Contract Handling
- Protocol Contract Uses Permit:
- The
Protocol Contractprocesses Alice’s interaction request and forwards the permit message (msg, sig) to theERC2612token contract. - The
ERC2612contract verifies the signature and the details in the permit message to ensure it is valid and that Alice indeed authorized the transaction.
- The
Token Transfer
- ERC2612 Executes Transfer:
- Upon successful verification, the
ERC2612token contract executes thetransferFrom()function. - This function transfers the specified amount of tokens from Alice’s account to the recipient as directed by the
Protocol Contract.
- Upon successful verification, the
Summary
- Off-Chain Signing: Alice signs a permit message off-chain, which authorizes the transfer of her tokens.
- Interaction Request: Alice sends an interaction request to the
Protocol Contract, including the signed permit. - Permit Verification and Transfer: The
Protocol Contractforwards the permit to theERC2612contract, which verifies the permit and then transfers the tokens usingtransferFrom().
This workflow allows Alice to authorize token transfers without having to send an on-chain transaction for approval, thereby saving gas costs and simplifying the user experience. The use of the permit mechanism ensures that the token transfer is secure and only happens with Alice’s explicit consent.
The big limitation of ERC-2612 is that it works only for the tokens that implement it. All the other tokens cannot be processed through this clever process.
Permit Anywhere: The way to make token permissions available to any token.
Summary of PermitEverywhere
PermitEverywhere is a set of smart contracts enabling permit-style approvals for all ERC20 and ERC721 tokens, regardless of whether they implement EIP2612. Users set allowances on ERC20PermitEverywhere or ERC721PermitEverywhere contracts, allowing protocols to accept signed permit messages for secure fund transfers without explicit allowances on their contracts. These messages use EIP712 for human-readable signing via popular web3 wallets. The project laid the groundwork for Uniswap’s Permit2, offering a lean and gas-optimized implementation.
For more details, visit the GitHub repository.
Step-by-Step Workflow with PermitEverywhere
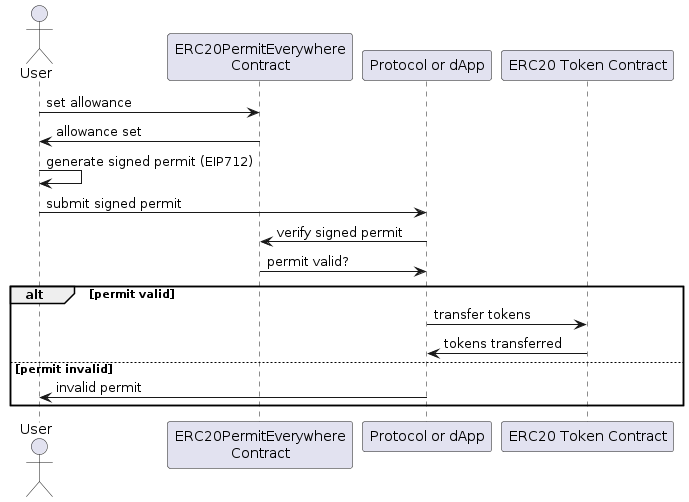
- Setup Allowance:
- User sets allowances on
ERC20PermitEverywhereorERC721PermitEverywherecontracts. This is done by sending a transaction to theapprovemethod on thePermitEverywherecontract.
- User sets allowances on
- Generate Permit:
- The user generates a signed permit message using their private key. This message follows the EIP712 standard, which ensures human-readable data for signing.
- Submit Permit:
- The user submits the signed permit message to the protocol or dApp they wish to interact with. This permit message authorizes the transfer of tokens without needing to approve the token contract explicitly.
- Verify and Execute:
- The receiving protocol or dApp verifies the signed message using the
PermitEverywherecontract. If valid, it allows the transfer of the specified tokens as per the user’s permit.
- The receiving protocol or dApp verifies the signed message using the
- Token Transfer:
- The transfer of tokens is executed according to the permissions set in the permit message, ensuring that the transaction complies with the user’s signed authorization.
- Completion:
- The tokens are transferred to the designated recipient, completing the workflow securely and efficiently without multiple approval transactions.
Permit2. The permit solution from Uniswap Labs
Python Anywhere has been of guidance and inspiration for the birth of a similar protocol aimed at being integrated in the future architectures of Uniswap.
The diagram provided illustrates the workflow involving the Permit2 protocol and ERC20 token transfers. It shows how Permit2 allows for more streamlined and gas-efficient token transfers by leveraging off-chain signed messages.
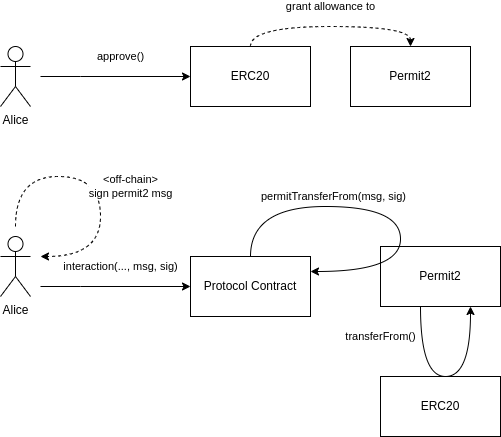
Here’s a step-by-step explanation:
Setting Up Allowance
- Alice Approves Allowance:
- Alice (represented by the user icon on the left) initiates the process by calling the
approve()function on theERC20token contract. - This function call grants an allowance to the
Permit2contract, authorizing it to spend a specified amount of Alice’s ERC20 tokens on her behalf.
- Alice (represented by the user icon on the left) initiates the process by calling the
- ERC20 Contract Updates Allowance:
- The
ERC20contract updates its records to reflect that thePermit2contract is permitted to spend Alice’s tokens up to the approved amount.
- The
Generating and Using the Permit
- Alice Signs Permit2 Message (Off-Chain):
- Alice generates a permit message off-chain. This message includes details such as the amount of tokens to be transferred and the recipient’s address.
- Alice signs this permit message using her private key. The signature (
sig) authenticates her consent for the specified transaction.
- Alice Initiates Interaction with Protocol:
- Alice sends an interaction request to the
Protocol Contract. This request includes the signed permit message (msg, sig) and any other necessary parameters. - This step effectively submits her intent to authorize the protocol to use her tokens as per the signed permit.
- Alice sends an interaction request to the
Permit2 Contract Handling
- Protocol Contract Uses Permit2:
- The
Protocol Contractprocesses Alice’s interaction request and forwards the permit message (msg, sig) to thePermit2contract. - The
Permit2contract verifies the signature and the details in the permit message to ensure it is valid and that Alice indeed authorized the transaction.
- The
Token Transfer
- Permit2 Executes Transfer:
- Upon successful verification, the
Permit2contract calls thetransferFrom()function on theERC20contract. - This function transfers the specified amount of tokens from Alice’s account to the recipient as directed by the
Protocol Contract.
- Upon successful verification, the
Summary
- Allowance Approval: Alice grants allowance to the
Permit2contract to spend her ERC20 tokens. - Off-Chain Signing: Alice signs a permit message off-chain, which authorizes the transfer of her tokens.
- Interaction Request: Alice sends an interaction request to the
Protocol Contract, including the signed permit. - Permit Verification and Transfer: The
Protocol Contractforwards the permit to thePermit2contract, which verifies the permit and then transfers the tokens usingtransferFrom().
This workflow allows Alice to authorize token transfers without having to send multiple on-chain transactions, thereby saving gas costs and simplifying the user experience. The use of Permit2 ensures that the token transfer is secure and only happens with Alice’s explicit consent through the signed permit message.
Conclusions: Pros and Cons of Permit Anywhere, Permit2, and ERC2612
Permit Anywhere
Pros:
- Universal Compatibility: Works with all ERC20 and ERC721 tokens, regardless of whether they implement EIP2612.
- Enhanced User Experience: Simplifies the approval process by enabling off-chain signing, reducing the number of on-chain transactions.
- Gas Savings: Significant reduction in gas costs since users don’t need to perform multiple on-chain approval transactions.
Cons:
- Complex Implementation: Requires additional infrastructure to handle off-chain signatures and validate them on-chain.
- Security Concerns: Managing off-chain signatures securely can be challenging and may introduce new attack vectors if not handled properly.
- Initial On-Chain Approval: Users must still approve the PermitAnywhere contract initially, which involves an on-chain transaction.
Permit2
Pros:
- Gas-Efficient: Allows for gasless transactions by leveraging signed permits, which can be particularly beneficial during periods of high network congestion.
- Streamlined Workflow: Users can set allowances once and use signed permits for multiple interactions, improving the efficiency of token transfers.
- Advanced Features: Built on the Uniswap ecosystem, it offers a robust and well-audited implementation.
Cons:
- Learning Curve: Users and developers may need time to adapt to the new workflow and understand how to use the permit functionality effectively.
- Dependency on Uniswap Ecosystem: Primarily designed for use within the Uniswap ecosystem, which may limit its applicability in other contexts initially.
- Initial On-Chain Approval: Users must initially approve the Permit2 contract, which requires an on-chain transaction.
ERC2612
Pros:
- Standardized Approach: As an Ethereum Improvement Proposal, it provides a standardized method for permit-based approvals, promoting interoperability.
- Widespread Adoption: Increasingly adopted by various projects, making it a well-recognized and supported standard in the DeFi community.
- Improved Security: Built-in mechanisms for securely handling off-chain signatures, reducing the risk of attacks compared to custom implementations.
- No On-Chain Approval Needed: Users are never required to approve with an on-chain transaction, eliminating the initial setup cost and simplifying the process.
Cons:
- Limited to Supporting Tokens: Only applicable to ERC20 tokens that implement the ERC2612 standard, which may limit its use with other tokens.
- Initial Setup Required: Projects need to integrate ERC2612 into their tokens, which may require additional development effort.
Final Thoughts
Each of these solutions offers unique benefits and addresses specific challenges in the DeFi space:
- Permit Anywhere is highly versatile and can be used with any ERC20 or ERC721 token, making it a flexible solution for various applications. However, it requires an initial on-chain approval to the PermitAnywhere contract.
- Permit2 provides an efficient and gas-saving approach, especially within the Uniswap ecosystem, but users must initially approve the Permit2 contract on-chain.
- ERC2612 offers a standardized and secure method for permit-based approvals, with the advantage that users are never required to perform an on-chain approval transaction, simplifying the user experience significantly.
By adopting these innovative solutions, the DeFi ecosystem can significantly enhance user experience, reduce costs, and streamline token interactions, driving greater adoption and growth. However, careful consideration of the pros and cons is essential to choose the most suitable solution for specific use cases.
References
Here is a list of references for the concepts mentioned:
Permit Anywhere
- GitHub Repository: Permit Everywhere - This repository provides an implementation of permit-style approvals for all ERC20 and ERC721 tokens, regardless of whether they implement EIP2612.
Permit2
- Uniswap Labs Blog: Introducing the UniswapX Protocol - This blog post discusses UniswapX and the Permit2 mechanism.
- GitHub Repository: Permit2 Implementation - This repository contains the code for the Permit2 system, which allows for gas-efficient and secure token transfers using signed permit messages.
ERC2612
- Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP) 2612: EIP-2612: permit - 712-signed approvals - This document details the specification for ERC2612, which extends the ERC20 standard to include a permit function, allowing approvals via off-chain signatures.
- GitHub Implementation: ERC2612 Implementation - An implementation of ERC2612 in the OpenZeppelin contracts library.
These references provide detailed information and code implementations for the Permit Everywhere, Permit2, and ERC2612 concepts, helping you understand their functionalities and applications in the Ethereum ecosystem.
